뉴스
고품질 고성능 우수한 서비스
제품 검색게시물 검색
고품질 고성능 우수한 서비스
Introduction: The Engine Room of Dentistry
In our previous discussion (귀하의 치과 진료는 다이오드 정밀성을 놓치고 있습니까?), we explored the clinical outcomes of laser surgery. But for medical device engineers, biomedical technicians, and OEM manufacturers, the clinical result is merely the final output of a complex chain of electronics.
The heart of any medical laser system is the 레이저 다이오드 모듈. However, a module is only as good as the current controlling it. The symbiotic relationship between the 레이저 다이오드 및 구동기 is the single most critical factor in device safety, longevity, and FDA/CE compliance. This article deconstructs the engineering required to build a reliable 치과용 다이오드 레이저.
The Anatomy of a High Power Laser Diode Module
A 고출력 레이저 다이오드 is a semiconductor device that converts electrical energy into coherent light. In dental applications, we typically operate in the Near-Infrared (NIR) spectrum (808nm to 1064nm).
Unlike telecommunication lasers, a dental 레이저 다이오드 모듈 requires massive photon density to ablate tissue. This introduces the “Thermal bottleneck.”
The Unsung Hero: The Laser Diode and Driver
You cannot simply plug a laser diode into a wall outlet. It requires a constant current source, not constant voltage. This is the job of the 레이저 다이오드 및 구동기.
Key Technical Requirements for Medical Drivers:
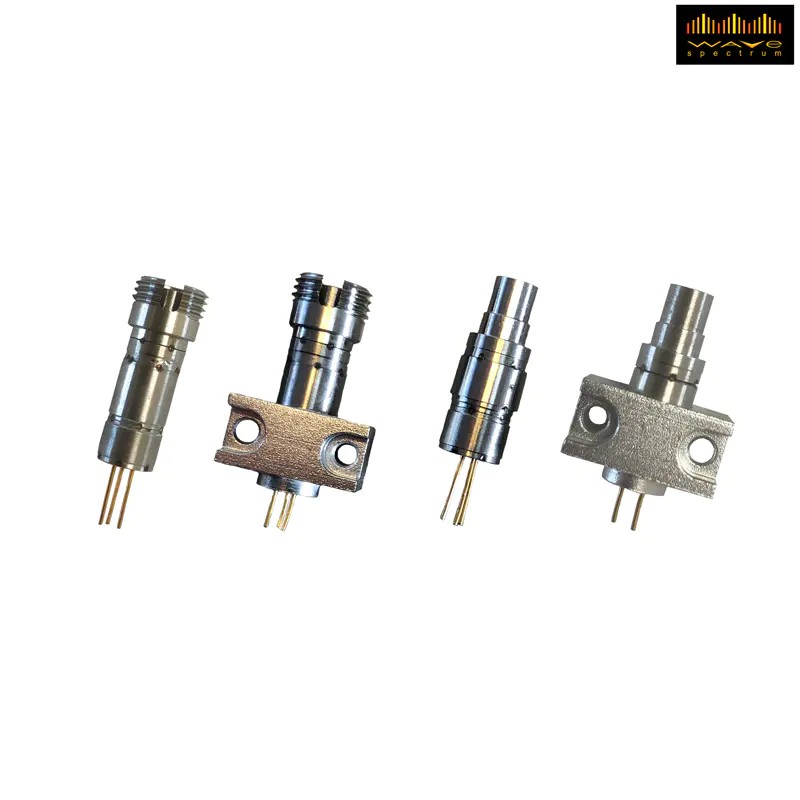
Technical Case Study: Failure Analysis of a Generic Unit (This section mimics an engineering failure report)
Incident Report: #ENG-2024-88 Device Type: 10W Portable 치과용 다이오드 레이저 (Imported Generic Brand). Problem: Device failing to initiate fiber tips; User reports “Fluctuating power” and “Device gets hot to touch.”
Forensic Disassembly & Analysis:
- Component A: 그 레이저 다이오드 모듈 was inspected. The collimating lens showed signs of fogging due to outgassing from cheap thermal paste.
- Component B: 그 레이저 다이오드 및 구동기 circuit was analyzed via oscilloscope.
- Findings:
- Ripple Current: The driver exhibited a 15% ripple current (Standard should be <1%).
- 열 관리: The diode was mounted on a passive aluminum block with no TEC (Thermoelectric Cooler).
The Failure Chain:
- As the dentist used the laser for a long procedure (full mouth decontamination), the passive cooling failed.
- The diode junction temperature rose.
- The driver, lacking active feedback loops, continued to push current.
- The combination of heat and ripple current caused “Facial Catastrophic Optical Damage” (COD) to the diode emitter.
- Result: The optical output dropped from 10W to 2W, rendering the device useless.
Correction Strategy: Replacing the unit with a module featuring an integrated NTC thermistor and a PID-controlled driver solved the issue, stabilizing output to ±0.1W.
Advanced Applications: Fiber Coupling Efficiency
For a 치과용 다이오드 레이저 to be effective, the light from the emitter must enter a fiber optic core that is often only 200 to 400 microns wide.
Future Trends: Blue Light and Multi-Wavelengths
The future of the 레이저 다이오드 모듈 industry is hybrid packaging. We are now seeing modules that combine 450nm (Blue – for superior cutting efficiency without heat) and 980nm (Infrared – for deep disinfection) into a single output. This requires a sophisticated multi-channel 레이저 다이오드 및 구동기 capable of mixing wavelengths in real-time.
Summary for Buyers and Engineers
When designing or purchasing a 치과용 다이오드 레이저, specifications on a datasheet are not enough. You must verify the quality of the 레이저 다이오드 및 구동기 integration. Stability, thermal management, and protection circuits are what differentiate a medical device that lasts 5 years from one that fails in 6 months. A robust 고출력 레이저 다이오드 system is an investment in reliability.
과학 실험실, 의료기기 기업, 산업용 측정 시스템 전반에 걸쳐 레이저 다이오드 모듈은 여전히 가장 중요한 광학 하위 시스템 중 하나입니다. 수요는 단순한 조명 도구에서 고도로 규제되고 열적으로 안정적인 솔루션으로 전환되었습니다.
상세 정보 보기산업용 포토닉스의 급속한 확장은 안정적이고 고출력이며 소형화된 레이저 솔루션에 대한 수요를 촉진시켰습니다. 이 중 레이저 다이오드 모듈은 감지, 정렬, 분광학, 통신 분야에서 핵심 구성 요소로 자리매김했습니다.
상세 정보 보기미용 의료 분야, 특히 제모 및 혈관 치료 시장에서 장비 가동 중단은 수익성을 저해하는 숨은 위협 요소입니다. 수년간 업계 표준은 무겁고 수냉식 수직 스택 핸드피스였습니다. 이...
상세 정보 보기현대 웨어러블 기기(스마트워치, AR 안경, TWS 이어버드)의 조립 과정에서 접착제와 초음파 용접이 점차 사라지고 있다. 접착제는 경화 속도가 너무 느리고, 초음파 진동은 민감한 MEMS 마이크로폰과 자이로스코프를 손상시키기 때문이다. 표준은 ...
상세 정보 보기